Understanding the Key Distinctions: Freefall vs. Standard Electric Windlass
 2025.10.17
2025.10.17
 Industry News
Industry News
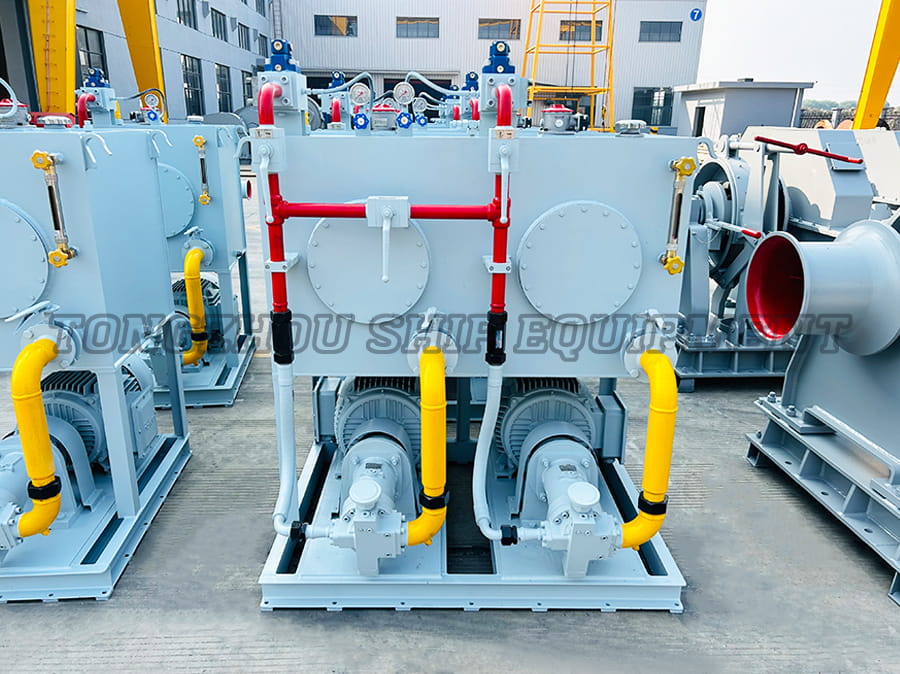
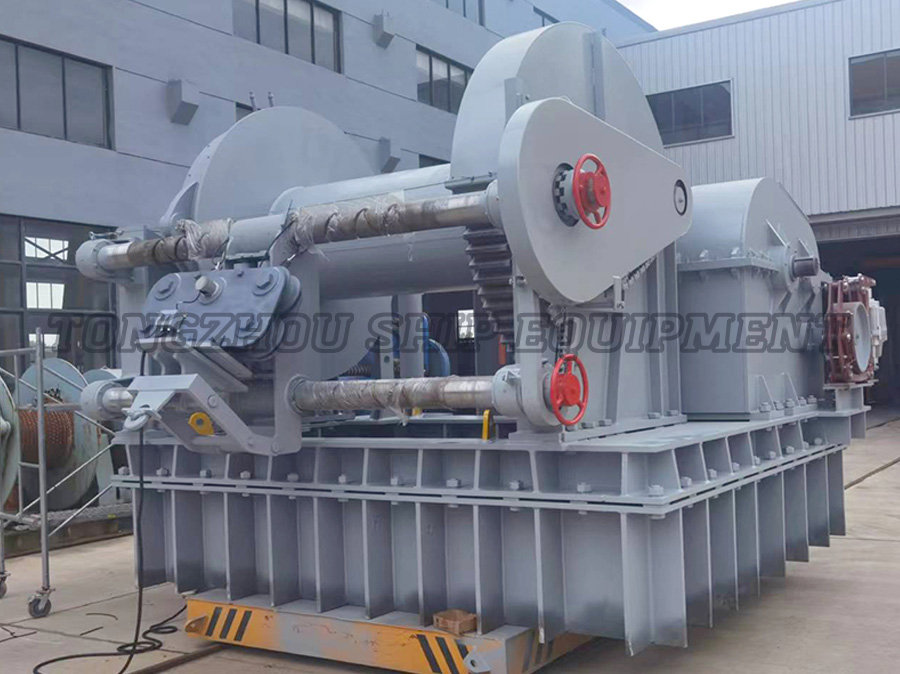
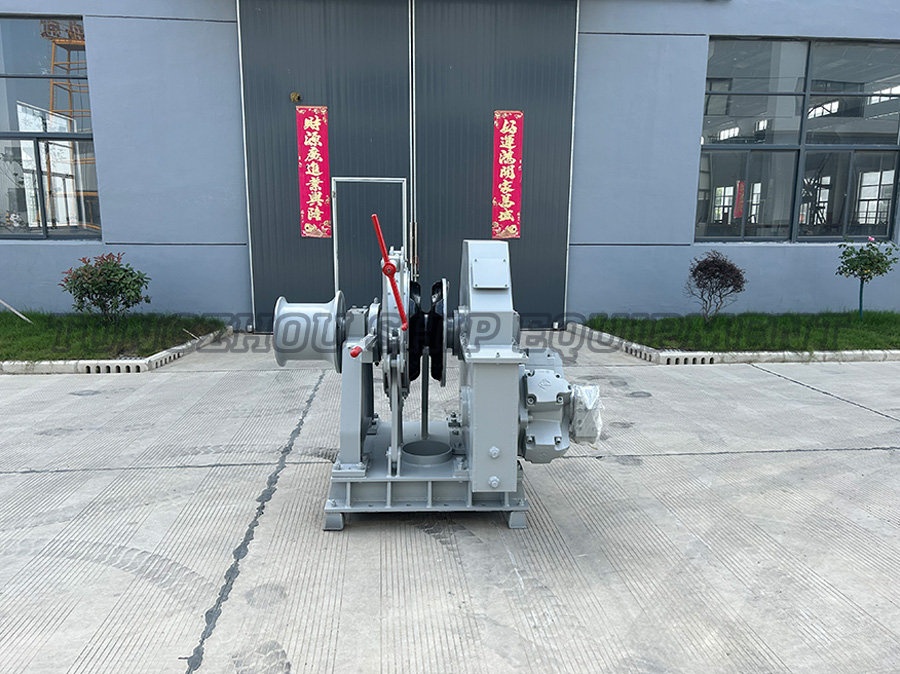
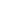
When it comes to marine anchoring systems, the choice between a freefall and a standard electric windlass can significantly impact vessel operations. An electric windlass is a motor-driven device used to raise and lower anchors and chains on boats, providing mechanical assistance for anchoring tasks.
What is an Electric Windlass?
An electric windlass is an essential component in modern boating, designed to handle heavy anchors and chains with electric power. It typically consists of a motor, gear system, and controls to facilitate efficient anchoring. Key aspects include:
-
Functionality: It automates the process of deploying and retrieving anchors, reducing manual effort.
-
Components: Common elements include a gypsy or wildcat for chain management and a circuit breaker for safety.
-
Applications: Electric windlasses are used in various vessels, from recreational boats to commercial ships, to enhance safety and convenience during anchoring.
Overview of a Standard Electric Windlass
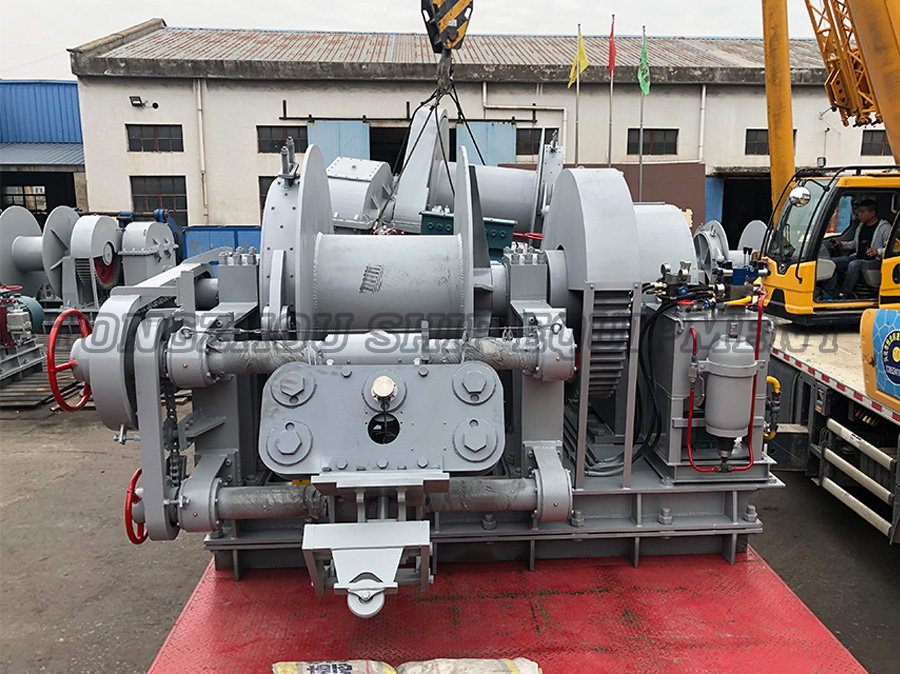
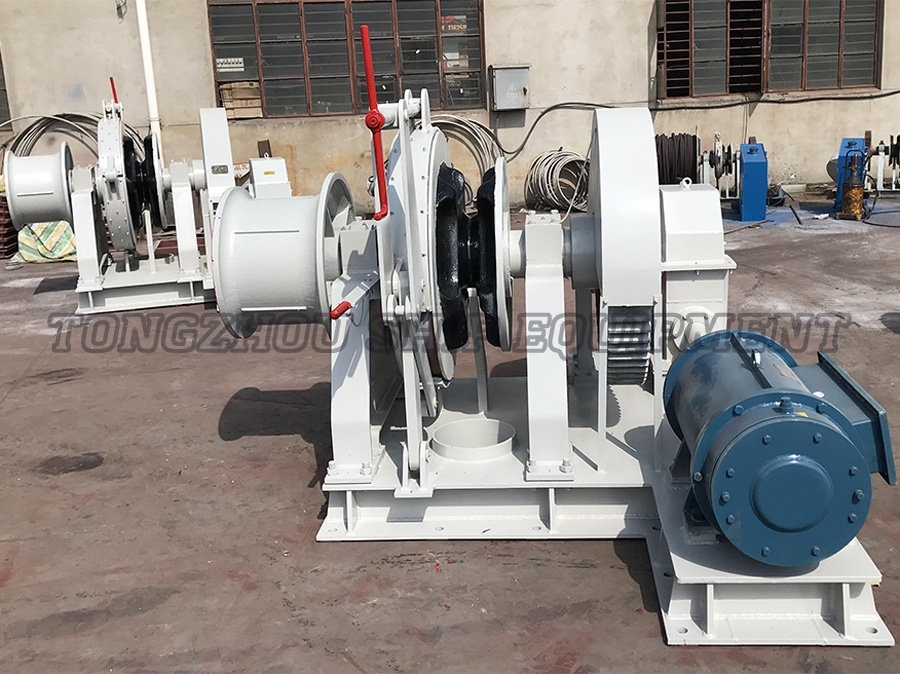
A standard electric windlass operates using electric power to control both the raising and lowering of the anchor. This type is widely employed due to its controlled operation and reliability. Notable features are:
-
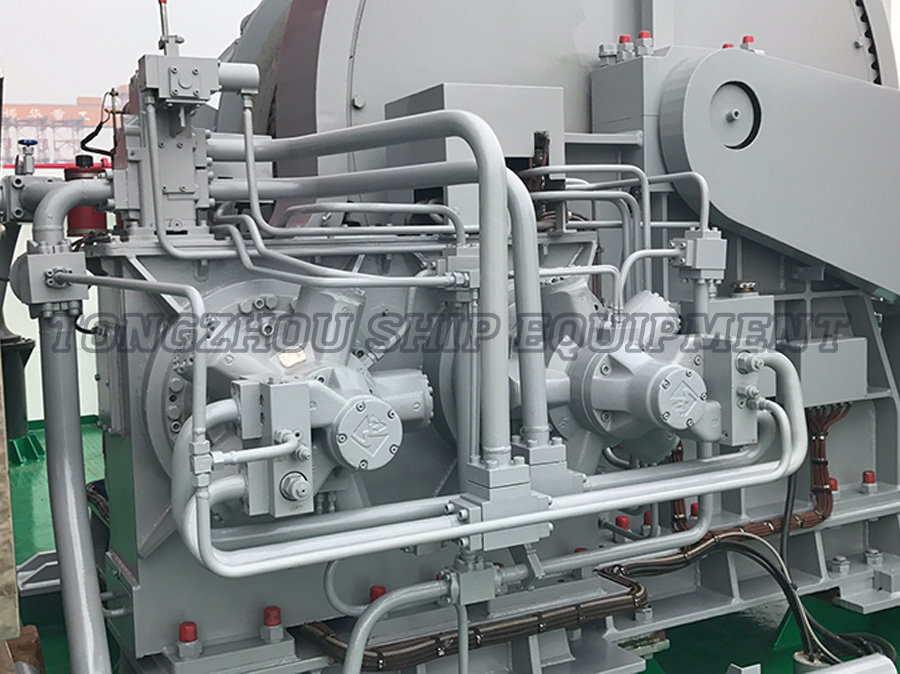
Operation Mechanism: The electric motor drives the windlass to hoist the anchor and can be used to lower it in a controlled manner, often through a clutch or brake system.
-
Advantages:
-
Provides precise control over anchor deployment, minimizing the risk of chain tangles or sudden drops.
-
Suitable for situations requiring gradual anchoring, such as in crowded marinas or delicate seabeds.
-
-
Limitations:
-
May consume more power during continuous operation.
-
Typically slower in deploying the anchor compared to freefall systems, especially in emergencies.
-
Overview of a Freefall Electric Windlass
A freefall electric windlass, also known as a freefall-capable windlass, incorporates a design that allows the anchor and chain to fall rapidly under gravity without relying on the electric motor for descent. This system combines electric hoisting with manual or assisted freefall. Key characteristics include:
-
Operation Mechanism: While the electric motor is used for raising the anchor, the lowering process often involves disengaging the clutch to enable a freefall mode, where gravity accelerates the deployment.
-
Advantages:
-
Enables quick anchor deployment, which is critical in emergency situations or when rapid anchoring is needed.
-
Reduces wear on the electric motor during lowering, potentially extending the system's lifespan.
-
-
Limitations:
-
Requires careful handling to avoid uncontrolled drops that could damage equipment or pose safety risks.
-
May not offer the same level of precision as a standard electric windlass for slow, controlled deployments.
-
Key Differences Between Freefall and Standard Electric Windlasses
The primary distinctions lie in their operational methods and suitability for different scenarios. Below is a comparative analysis:
-
Deployment Speed:
-
Freefall electric windlasses allow for faster anchor deployment due to gravity-assisted lowering.
-
Standard electric windlasses provide slower, motor-controlled deployment, ensuring gradual descent.
-
-
Control and Precision:
-
Standard electric windlasses offer enhanced control through electric regulation, making them ideal for precise anchoring.
-
Freefall electric windlasses prioritize speed over fine control, which can be advantageous in time-sensitive conditions.
-
-
Power Usage:
-
In standard electric windlasses, the motor is active during both raising and lowering, leading to consistent power consumption.
-
Freefall electric windlasses minimize power use during lowering by leveraging gravity, though the electric component is still essential for hoisting.
-
-
Maintenance and Durability:
-
Freefall systems may experience higher mechanical stress during rapid deployments, potentially requiring more frequent inspections.
-
Standard electric windlasses often have more complex electrical parts that need regular servicing to ensure reliability.
-
Considerations for Choosing the Right Electric Windlass
Selecting between a freefall and standard electric windlass depends on operational needs and vessel specifications. Factors to evaluate include:
-
Vessel Type and Size: Larger vessels might benefit from freefall capabilities for quick responses, while smaller boats may prefer the control of a standard electric windlass.
-
Anchoring Frequency: For frequent anchoring in varied conditions, a standard electric windlass provides versatility, whereas freefall is suited for infrequent but urgent deployments.
-
Safety Requirements: Assess the need for controlled descent versus rapid action, considering crew experience and typical anchoring environments.
The difference between a freefall and a standard electric windlass centers on deployment mechanisms and operational priorities. A standard electric windlass emphasizes controlled, electric-powered anchoring, while a freefall electric windlass integrates gravity-assisted lowering for speed. Understanding these distinctions helps in making informed decisions based on factual requirements, ensuring efficient and safe marine operations.



 English
English  عربى
عربى  中文简体
中文简体